Our paper in Theoretical Ecology was recently selected to be on F1000 Prime!
Critical transitions involve sharp changes in ecosystem states following small changes in driver variables. This could be for example, the sudden loss of a fishery as harvest rates of fish slowly increase. When these sharp changes cannot be reversed simply by going back to previous harvest rates, the system experiences hysteresis.
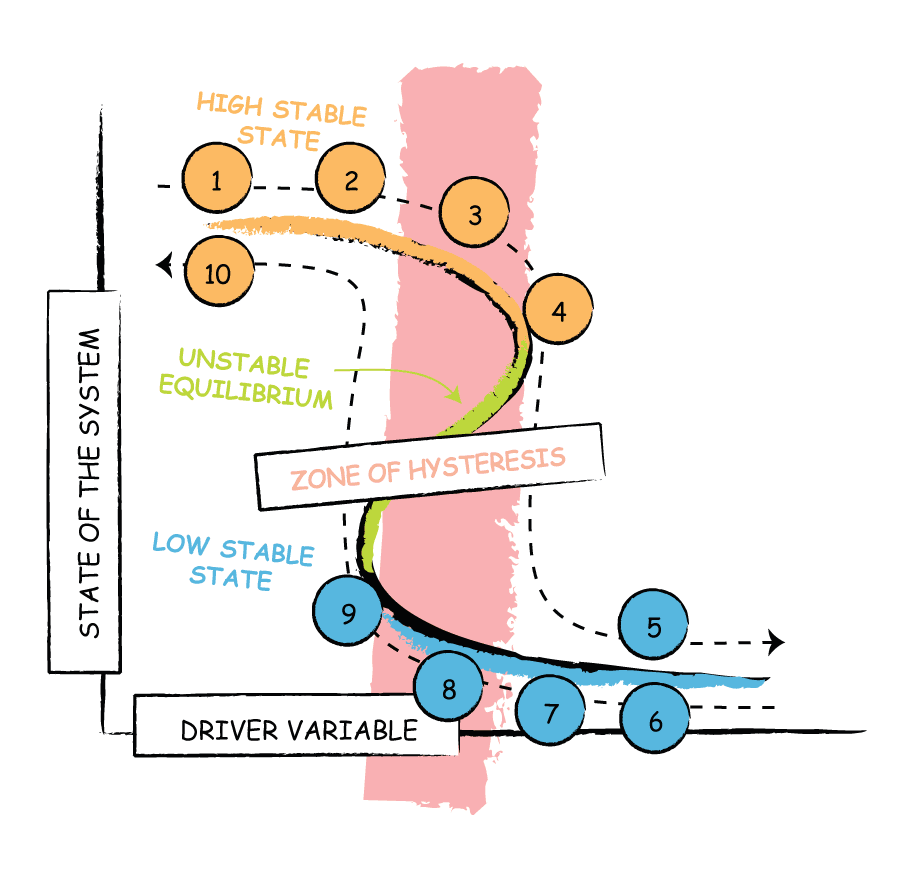 Most work in this area considers the effects of a single driver variable, although many systems are acknowledged to have multiple potentially interacting driver variables (in the example above, harvest rates and say, pollution). In this paper, we explore what happens when multiple driver variables are correlated.
Most work in this area considers the effects of a single driver variable, although many systems are acknowledged to have multiple potentially interacting driver variables (in the example above, harvest rates and say, pollution). In this paper, we explore what happens when multiple driver variables are correlated.
In short, a diversity of hysteretic patterns are possible. Some indicate that system states could be lost, trapped in hidden stable states like:
As we move forward we lose the desired ecosystem state, but moving backwards does not allow us to recover no matter how far we retreat.
Check out the review of the work, which describes complicated versions of hysteresis in simple population models.

