Reining in polyoma virus associated nephropathy: design and characterization of a template mimicking BK viral coat protein cellular binding.
Abstract
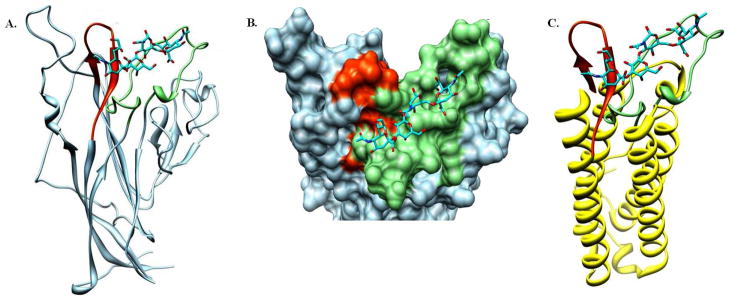
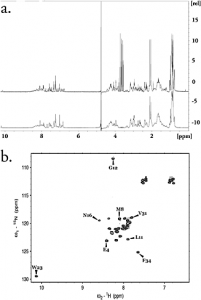
The BK polyoma virus is a leading cause of chronic post kidney transplantation rejection. One target for therapeutic intervention is the initial association of the BK virus with the host cell. We hypothesize that the rate of BKV infection can be curbed by competitively preventing viral binding to cells. The X-ray structures of homologous viruses complexed with N-terminal glycoproteins suggest that the BC and HI loops of the viral coat are determinant for binding and thereby infection of the host cell. The large size of the viral coat precludes it from common biophysical and small molecule screening studies. Hence, we sought to develop a smaller protein template incorporating the identified binding loops of the BK viral coat in a manner that adequately mimics the binding characteristics of the BK virus coat protein to cells. Such a mimic may serve as a tool for the identification of inhibitors of BK viral progression. Herein, we report the design and characterization of a reduced-size and soluble template derived from a four-helix protein-TM1526 of Thermatoga maritima archaea bacteria-which maintains the topological display of the BC and HI loops as found in the viral coat protein, VP1, of BKV. We demonstrate that the GT1b and GD1b sialogangliosides, which bind to the VP1 of BKV, also associate with our BKV template. Employing a GFP-tagged template, we show host cell association that is dose dependent and that can be reduced by neuraminidase treatment. These data demonstrate that the BKV template mimics the host cell binding observed for the wild-type virus coat protein VP1.